Uterine fibroids are benign tumors that develop either inside or outside the uterus, affecting around 70%- 80% of women of childbearing age. While often harmless, fibroids can cause significant discomfort and complications, especially when they begin breaking down during fibroid degeneration.
Understanding the signs of fibroid degeneration is essential for managing your health, so in this article, we’ll discuss what fibroid degeneration is and how to recognize symptoms. Some of these symptoms include fever, lower back pain, irregular periods, frequent urination, and pelvic pain. Along with understanding fibroid degeneration, we’ll also cover coping strategies and treatment options that can help alleviate the stress of fibroid passage and promote a more comfortable process for you.
If you think you have fibroids but aren’t sure, our symptom checker can help determine whether you should visit a healthcare professional for a diagnosis.
Understanding Fibroids
Many women have fibroids and can experience anything from mild symptoms to severe, debilitating symptoms. When figuring out if what you are experiencing may be related to fibroids, these are some common symptoms you should watch out for:
- Fatigue, which may be anemia due to blood loss
- Bloating or an enlarged uterus
- Heavy bleeding during the menstrual cycle
- Abdominal pain and cramps
- Frequent urination
Fibroids can manifest in various types and forms, each with distinct characteristics and symptoms, which include:
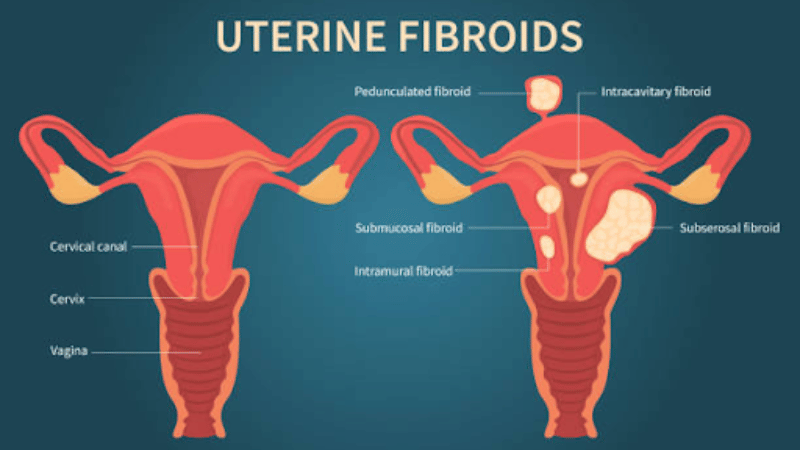
- Intramural Fibroids: The most commonly diagnosed fibroids, these fibroids grow within the muscular walls of the uterus and present symptoms such as heavy and prolonged periods, pelvic discomfort, lower back pain, or irregular bleeding.
- Subserosal Fibroids grow outside the uterus, causing pelvic or abdominal heaviness, frequent urination, constipation, abdominal pain, and an expanded abdomen resembling pregnancy.
- Submucosal Fibroids: Submucosal fibroids develop within the inner lining of the uterus, with symptoms such as heavy menstruation, bleeding between periods, anemia, and pelvic or lower back pain.
- Pedunculated Fibroids: Attached to the uterine wall by a stalk and can be subserosal (outside the uterus) or submucosal (inside the uterus). If the fibroid rotates on its stalk, disrupting blood flow, it may cause sharp, stabbing pains.
- Calcified Fibroids: When fibroids outgrow their blood supply, they can undergo degeneration, resulting in calcium deposits and hardening of the tissue. Symptoms may include frequent urination, constipation, and severe abdominal pain or pressure.
If you experience any combination of these symptoms, visit a fibroid specialist for an accurate assessment and personalized care.
What is Fibroid Degeneration?
Fibroid degeneration, or fibroid sloughing, is when fibroids break down through cell death. Since fibroids are made up of living cells, they require oxygen and other nutrients in the blood, typically coming through a uterine artery and attached blood vessels. Degeneration starts when fibroids stop receiving enough of these nutrients, causing the cells to die off until the tumor is a more sustainable size.
Different types of degeneration depend on the degree and the rapidity of vascular insufficiency. Types of degenerating fibroids include:
- Hyaline Degeneration: The most common type involves replacing normal connective tissue and smooth muscle fibers with hyaline tissue, which gives the fibroid a glassy appearance.
- Calcification: The formation of calcium deposits as fibroid tissue dies off may lead to a hardened, non-functioning fibroid. Calcification is more likely to occur in older women.
- Cystic Degeneration: This condition is more likely to occur after menopause. It involves the formation of cysts on a fibroid, which, under microscopic examination, resemble ovarian cysts.
- Myxoid Degeneration: The replacement of smooth tissue with a jelly-like substance characterized by transparent connective tissue with a mucus-like appearance.
- Red Degeneration: A severe form often observed during pregnancy. Red degeneration occurs when a blood vessel ruptures or the blood supply is restricted, causing internal bleeding.
Is Fibroid Degeneration a Good Thing?
Fibroid degeneration can have some benefits and some drawbacks. Degeneration can reduce a fibroid’s size while offering relief from associated symptoms.
However, the process can be painful, causing acute pelvic discomfort while the fibroid passes. Although fibroid degeneration may provide temporary symptom relief, fibroids can grow back or continue to cause issues in the future, necessitating further treatment. In rare cases, degeneration can lead to complications such as infection or hemorrhage, so working with a fibroid specialist is necessary, especially when fibroids are passing.
What Happens When a Fibroid Breaks Down?
Fibroids require a steady blood and oxygen supply to grow. One of the most typical causes of a fibroid breaking down is inadequate blood supply (ischemia). Ischemia is usually a result of the fibroid growing too large or experiencing mechanical compression of feeder arteries.
Additionally, as fibroids shrink, they can cause abnormal and severe bleeding, which may differ from a woman’s usual menstrual bleeding pattern. If you notice abnormally heavy bleeding, we recommend seeking immediate medical care to address potential complications associated with fibroid degeneration.
LEARN MORE ABOUT YOUR HEALTH IN OUR NEWSLETTER
How Do You Know if Fibroids Are Breaking Down?
The symptoms of fibroids shrinking are notably different and more intense compared to typical fibroid symptoms. One significant indicator of fibroid degeneration is a severe stabbing-like pain in the abdomen, often accompanied by swelling. This pain occurs as the fibroid shrinks and its cells begin to die off, releasing chemicals into the abdominal cavity.
Other common signs of fibroids passing are:
- Pelvic and lower back pain
- Fever
- Pain during intercourse
- Irregular periods or spotting in between periods
- Frequent urination or even difficulty urinating
- Constipation
- Bloating
- Watery discharge or a pinkish tinge
- Elevated white blood cell counts
If you notice any combination of these symptoms, consult a medical professional to determine whether you are dealing with fibroid degeneration or possibly another medical issue.
Impact on Fertility and Pregnancy
Fibroids are thought to impact fertility and pregnancy in women, leading to difficulties in conceiving and increasing the risk of pregnancy complications. Having fibroids passing during pregnancy (necrobiosis) can result in abnormal bleeding and severe abdominal pain. This degeneration may occur due to the distortion and kinking of blood vessels by the enlarging uterus.
Pedunculated fibroids are particularly susceptible to degeneration, which can cause intense and prolonged pain. During pregnancy, fibroids are more likely to experience red degeneration, which can lead to internal bleeding.
A common sign of fibroid degeneration during pregnancy is a mild fever, as the degeneration process can trigger an inflammatory response. Women dealing with necrobiosis degeneration should get immediate medical attention for the safety of both her and the baby.
How to Handle Fibroid Degeneration

Managing fibroid degeneration can be pretty painful and negatively impacts one’s mental health. A few ways to cope with the symptoms of fibroids shrinking include:
- Mindfulness techniques
- Engaging in comforting activities
- Seeking support from friends, family, or support groups
- Accessing reliable information and resources
When dealing with fibroids, it’s important to prioritize self-care through a healthy diet, regular exercise, adequate rest, and stress management to avoid exacerbating symptoms.
Fibroid Degeneration Treatment
Although dealing with a fibroid breaking down and its accompanying symptoms can be challenging, various treatments are available. Over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen can temporarily relieve the painful symptoms of fibroids shrinking.
However, it’s better to consider treatment for your fibroids for a more long-term solution. Treatments such as uterine fibroid embolization (UFE) can help keep fibroid pain and other debilitating symptoms under control so you can live a more fulfilling life.
UFE is a minimally invasive fibroid treatment where a fibroid specialist uses an ultrasound to locate the fibroids before inserting a tiny catheter into the thigh or wrist. Embolic materials are injected into the artery, feeding the fibroid and blocking its nutrient supply. UFE blocks nutrients to the fibroids, just like fibroid degeneration, but in a more controlled environment to reduce the impact of the symptoms.
Take Care of Your Fibroids Before They Break Down
At USA Fibroid Centers, our UFE treatment helps women eliminate their fibroids and improve their overall well-being. While managing symptoms at home may provide temporary relief, seeking professional treatment can break the cycle of fibroid degeneration and prevent additional suffering.
Call us today at 855.615.2555 or schedule an appointment online.



