
The term “fibroid cyst” is a misconception. Ovarian cysts and uterine fibroids are two distinct conditions that affect the female reproductive system with fundamentally different symptoms, causes, complications, and treatment options.
Understanding the difference between uterine fibroids versus ovarian cysts can help when seeking a diagnosis and treatment options for symptoms such as pelvic pain and heavy bleeding.
If you’re feeling uncertain about whether you have uterine fibroids or ovarian cysts, a consultation with an interventional radiologist from USA Fibroid Centers can help clarify your concerns.
The Difference Between Ovarian Cysts and Fibroids
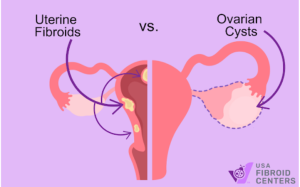
Ovarian cysts and uterine fibroids share a few similar symptoms but are located in different parts of the female reproductive system, have different compositions, and have different risk factors.
One difference between an ovarian cyst and a fibroid tumor is what causes them to form. For example, while the exact cause of fibroids is unknown, studies have shown connections between genetics, obesity, and ethnicity.
In comparison, ovaries naturally form cysts, or follicles, each month during ovulation. Two common types are corpus luteum cysts, which occur when fluid builds up in a follicle after it releases an egg, and follicular cysts, which form when a follicle doesn’t release its egg and continues to grow.
Fibroids vs. Cysts: Location
The biggest difference between uterine fibroids and ovarian cysts is where they grow. Fibroids develop inside the uterus or on the uterine walls, while ovarian cysts grow within the ovaries. If multiple cysts are growing within the ovaries, it can also be a symptom of PCOS.
Fibroids vs. Cysts: Composition and Structure
Aside from where they grow, their composition is another difference between an ovarian cyst and a fibroid tumor. Uterine fibroids are firm, dense, noncancerous tumors composed of smooth muscle cells and fibrous connective tissue, which can vary in size, location, and number. However, an ovarian cyst is made up of fluid, tissue or germ cells.
Ovarian cysts are not generally a cause for concern, but these growths can burst, causing debilitating pain. If you begin to notice symptoms that are painful or disruptive to your daily life, it’s best to consult a specialist to determine if you have uterine fibroids or ovarian cysts.
Find a Fibroid Specialist Near You
Fibroids vs. Cysts: Risk Factors
Fibroids’ risk factors include harming surrounding organs, impacting fertility, and causing painful and uncomfortable symptoms.
Ovarian cysts often resolve on their own without causing discomfort. However, larger cysts can lead to pain and pressure symptoms, along with serious complications such as:
- Ovarian torsion: The ovary twists and disrupts blood flow
- Ovarian rupture: Sudden, severe pain, fever, or vomiting, both of which require immediate medical attention.
Fibroids are almost always noncancerous, with only rare cases of them developing into cancer. However, certain types of ovarian cysts can sometimes be associated with cancer, particularly in postmenopausal individuals. When ovarian cysts are persistent and grow larger, a biopsy is recommended to determine the best treatment.
Ovarian Cyst vs. Fibroids Symptoms

Understanding the difference between ovarian cysts vs. fibroid symptoms is important for identifying these common gynecological conditions and seeking timely treatment.
Both conditions can occur in the reproductive system, potentially cause an enlarged uterus, and are often benign. However, uterine fibroids and ovarian cysts have similar symptoms, so it’s important to track your symptoms and bring them to a specialist to diagnose the condition.
To start you on a path to relief, USA Fibroid Centers offers a free fibroid symptom checker to help you determine whether you should visit a fibroid specialist for a diagnosis.
Fibroid Symptoms
Every person experiences fibroids differently. While some women may not notice any symptoms, others may struggle with chronic pain that negatively impacts their daily lives. The symptoms may vary based on the location and size of the fibroids.
Fibroid symptoms may include:
- Heavy periods lasting more than 10 days per month
- Fatigue caused by anemia
- Bleeding between menstrual cycles
- Pain during sex
- Protruding belly or abdominal area
- Severe pelvic pain or cramps
- Frequent urination or difficulty emptying your bladder
If you experience persistent or disruptive symptoms, consulting a fibroid specialist from USA Fibroid Centers can help diagnose and manage symptoms through treatment like uterine fibroid embolization (UFE)
Are you worried about fibroid diagnosis? Learn more here.
Ovarian Cyst Symptoms
A differential diagnosis between uterine fibroids and ovarian cysts can be made by carefully considering the presenting symptoms. Ovarian cyst symptoms often include:
- Pelvic pain or pressure on one side
- Abdominal bloating or a protruding belly
- Difficulty urinating
- Pain during sex
- Unexplained weight gain
- Breast tenderness
- Sharp, sudden abdominal pain
As the cyst grows, it can put pressure on surrounding tissues, increasing these symptoms.
Diagnosis of Fibroids and When to Seek Help

A fibroid specialist can help you determine a diagnosis and find the best treatment for your condition. Although there are various distinctions between uterine fibroids vs. ovarian cysts, both can be detected during a pelvic exam, typically accompanied by a medical history review.
If your medical provider or specialist believes you have ovarian cysts or uterine fibroids after a pelvic exam, they will order a pelvic ultrasound or other minimally invasive imaging to confirm your diagnosis.
These advanced tools enable fibroid specialists to pinpoint the exact location of fibroids through a technique known as fibroid mapping. Your treatment plan will be tailored to the specific characteristics of your fibroids, effectively eliminating your symptoms.
For both conditions, it can be helpful to track menstrual changes and symptoms like cramps and bloating to determine whether they are normal or could be caused by something else. If these changes persist over a few menstrual cycles, or if you notice any symptoms such as severe pelvic pain or bloating, visit a fibroid specialist for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment, like UFE.
Find Relief Today – Book Online
Treatment Options for Fibroids
If you’ve been diagnosed with fibroids, uterine fibroid embolization (UFE) is a treatment option provided by USA Fibroid Centers. This minimally invasive outpatient procedure targets the blood supply to your fibroid, effectively shrinking it and alleviating symptoms. UFE preserves the uterus and fertility, does not require general anesthesia or stitches, and has a shorter recovery time than surgery.
Seek Help From USA Fibroid Centers
Understanding the difference between uterine fibroids and ovarian cysts makes it easier to seek help to treat symptoms of either condition.
If you are experiencing any potential fibroid symptoms, consult a USA Fibroid Centers specialist regarding your symptoms or menstrual changes. Even if you are experiencing mild symptoms, UFE’s noninvasive nature means you can treat them and not have to manage any discomfort or pain anymore.
Schedule an appointment today online or by calling 855.615.2555, or use our location map to find your nearest location.
FAQs
Is an Ovarian Cyst More Dangerous than Fibroids?
Ovarian cysts and fibroids differ in their risks and potential complications. Ovarian cysts are generally considered more potentially dangerous due to a small risk of malignancy, though most are benign. Ovarian cysts often don’t need treatment since they resolve on their own, while fibroids typically require intervention based on their size and symptoms. Both conditions cause similar symptoms, but ruptured ovarian cysts can be severe, whereas fibroid complications usually stem from their impact on surrounding organs.
Can Fibroids Grow in the Ovaries?
Fibroids grow in or on the uterus and consist of muscle and connective tissue, not in the ovaries, but they can block the fallopian tubes, potentially impacting fertility.
Can You Have Fibroids and Ovarian Cysts at the Same Time?
Fibroids and ovarian cysts can develop in different locations, so it is possible to have both conditions simultaneously. Even though they may share similar symptoms, a doctor can diagnose and treat each condition separately if they present simultaneously. Ovarian cysts form in the ovaries, while fibroids form within or outside the uterus.
Do Fibroids Cause Ovarian Cysts?
Fibroids do not cause ovarian cysts, as they are two distinct gynecological conditions that affect different parts of the female reproductive system. While they may share overlapping symptoms like pelvic pain and irregular bleeding, their causes, locations, and specific presentations vary. Many women are at risk of developing one or both conditions at some point, highlighting the importance of accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment.
Fibroids vs. Cysts in Ovaries: Are They the Same?
Fibroids and ovarian cysts are different conditions that can cause similar symptoms, such as pelvic pain and abdominal protrusion. However, fibroids often cause heavy or painful periods, abnormal bleeding, and urinary or menstrual issues, whereas cysts typically result in pelvic pain, difficulty urinating, or breast tenderness.
Treatments for these conditions vary, as fibroids can be treated through uterine fibroid embolization (UFE), while ovarian cyst treatment can consist of medication, drainage, or surgical removal.



